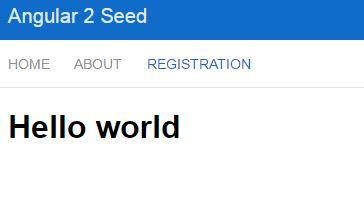
How to create registration form with Angular 2 seed
Angular Seed
If you are new to Angular 2 it is probably good idea to use some tool, which can help you out with all the settings required to run Angular.
This Angular Seed project by mgechev is a good way for you to start.
In this article we won’t write our Angular 2 registration form from scratch, but we will use the seed instead.
If you are already familiar with its structure, jump directly to Registration Form
Creating new unit
First, we will take a look at the structure of the seed and see how we should create new module and component for our registraion form.
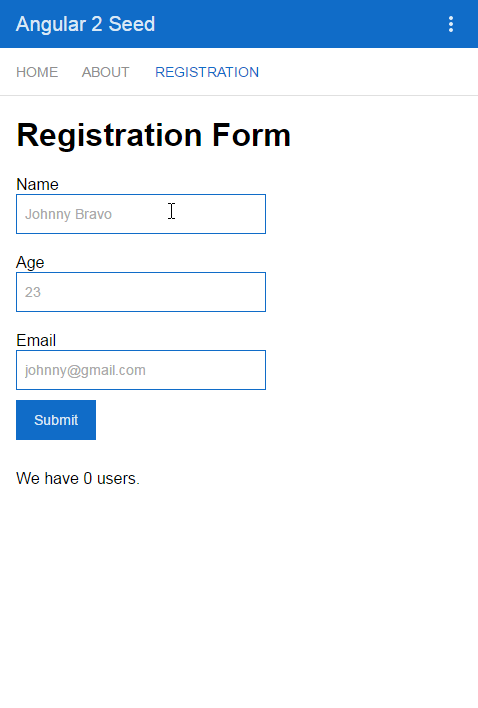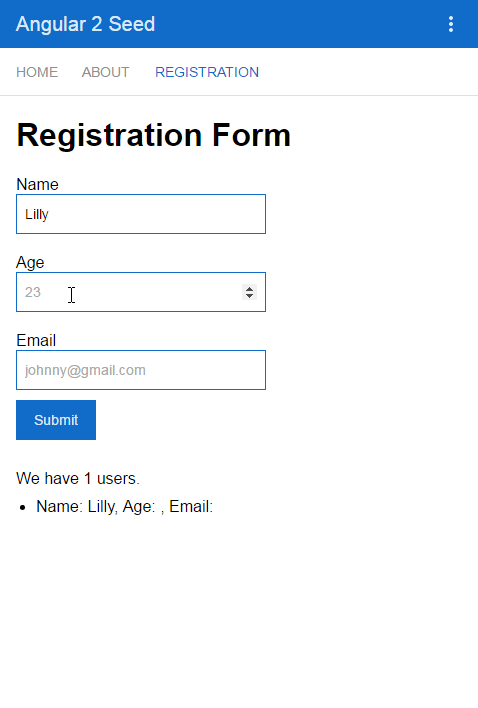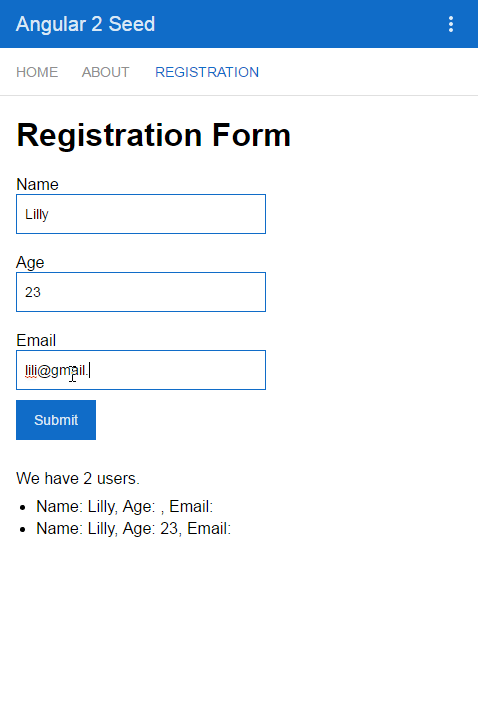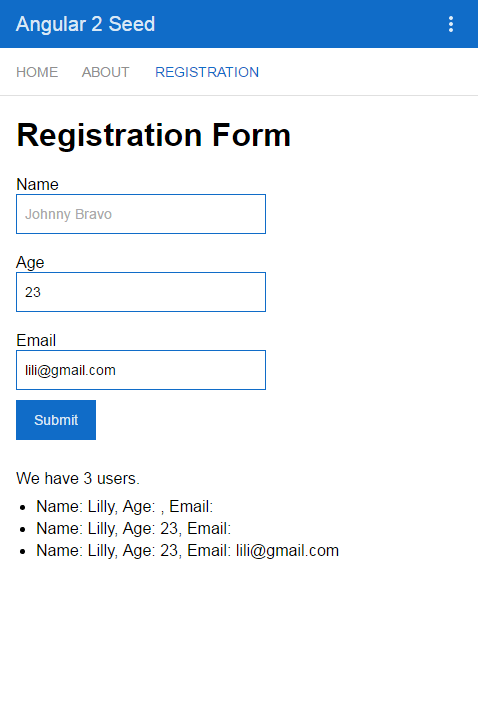
At the moment our goal is to create something like this:
Registration page
In order to reach our first goal we should create new folder ‘registration’ in app folder, with the following files:
- registration.module.ts
- registration.component.ts
- registration.component.html
- registration.component.css
- registration.routes.ts
- index.ts
1) Let’s start with the module file ‘registration.module.ts’.
Since we are aiming to create a registration form, we will directly import FormsModule in the file and in the decorator:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { RegistrationComponent } from './registration.component';
@NgModule({
imports: [CommonModule, FormsModule],
declarations: [RegistrationComponent],
exports: [RegistrationComponent]
})
export class RegistrationModule { }
2) Create Component for this module - registration.component.ts:
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
moduleId: module.id,
selector: 'sd-registration',
templateUrl: 'registration.component.html',
styleUrls: ['registration.component.css']
})
export class RegistrationComponent { }
3) Create an index file, which will export all of the components from our module - index.ts
export * from './registration.component';
export * from './registration.routes';
4) Route file registration.routes.ts
import { Route } from '@angular/router';
import { RegistrationComponent } from './index';
export const RegistrationRoutes: Route[] = [
{
path: 'registration',
component: RegistrationComponent
}
];
After we finish with files creation we need to make sure that everything is bind together
5) We need to add our module to app.module.ts
We need to be careful not only to import the RegistrationModule in the file, but to declare it in @NgModule decorator.
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { APP_BASE_HREF } from '@angular/common';
import { RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
import { HttpModule } from '@angular/http';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { routes } from './app.routes';
import { AboutModule } from './about/about.module';
import { HomeModule } from './home/home.module';
import { RegistrationModule } from './registration/registration.module';
import { SharedModule } from './shared/shared.module';
@NgModule({
imports: [BrowserModule, HttpModule, RouterModule.forRoot(routes), AboutModule, HomeModule, RegistrationModule, SharedModule.forRoot()],
declarations: [AppComponent],
providers: [{
provide: APP_BASE_HREF,
useValue: '<%= APP_BASE %>'
}],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
6) Add our route file to app.routes.ts
According to the design of the seed we have a variable containing our routes…
import { Routes } from '@angular/router';
import { AboutRoutes } from './about/index';
import { HomeRoutes } from './home/index';
import { RegistrationRoutes } from './registration/index';
export const routes: Routes = [
...HomeRoutes,
...AboutRoutes,
...RegistrationRoutes
];
7) Finally, we need to declare in the navbar.component.html file (placed in the ‘shared’ folder ) a link to the new page:
<nav>
<a [routerLink]="['/']" [routerLinkActive]="['router-link-active']" [routerLinkActiveOptions]="{exact:true}">HOME</a>
<a [routerLink]="['/about']" [routerLinkActive]="['router-link-active']" [routerLinkActiveOptions]="{exact:true}">ABOUT</a>
<a [routerLink]="['/registration']" [routerLinkActive]="['router-link-active']" [routerLinkActiveOptions]="{exact:true}">REGISTRATION</a>
</nav>
Registration
In the second part of this tutorial we will concentrate on creating our Template-Driven Form
First we will create file person.ts, where we will define different properties:
export class Person {
constructor(
public name: string,
public email: string,
public age: number
) { }
}
After that we will modify our already created registraition.component.ts file:
Everytime when our form is submitted, the new person will be added to an array or persons, which we will display later.
We also define a function, called onSubmit with parameter value, which is data, passed through the submitted form.
export class RegistrationComponent {
persons: Person[] = [];
counter = 0;
person: Person;
onSubmit(value) {
this.person = new Person(value.name, value.email, value.age);
if(value) {
this.persons.push(this.person);
}
this.counter++;
}
}
Back to our html template, we need to replace “Hello world” with actual form.
<div class="form">
<h1>Registration Form</h1>
<form #registrationForm="ngForm" (ngSubmit)="onSubmit(registrationForm.value)">
<div class='section'>
<label for="name" class="label">Name</label>
<input type="text" id="name" placeholder="Johnny Bravo" class="form-control" name="name" ngControl="name" #name="ngModel" ngModel required>
</div>
<div class="section">
<label for="age" class="label">Age</label>
<input type="number" id="age" placeholder="23" name="age" ngModel>
</div>
<div class="section">
<label for="email" class='label'>Email</label>
<input type="email" id="email" placeholder="[email protected]" name="email" ngModel>
</div>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
<div class="result">We have users.</div>
<ul><li *ngFor="let person of persons">Name: , Age: , Email: </li></ul>
</div>
There are few things that we need to consider here:
1) We should initiate our form #registrationForm=”ngForm”, so that we could pass its value on submition
2) For every input we should:
2.1) define a name
2.2) bind it with directive ngModel
3) At the end, we display the properties of every submitted person
If you like this, follow me on twitter!